The company can calculate the accumulated depreciation with the formula of depreciation expense plus the depreciated amount of fixed asset that the company have made so far. Depreciation expense will be calculated by the total cost of fixed assets less scrape value and divided by useful life. The original cost of the asset or its “basis” reflects all the costs to purchase the asset and put it to use for the business.A business will use one of two depreciation methods. The straight-line method calculates the depreciation at the same rate over time.
(In some instances they can take it all in the first year, under Section 179 of the tax code.) The IRS also has requirements for the types of assets that qualify. Depreciation is an accounting practice used to spread the cost of a tangible or physical asset over its useful life. Depreciation represents how much of the asset’s value has been used up in any given time period. Companies depreciate assets for both tax and accounting purposes and have several different methods to choose from.
Tax Savings
Together, we provide innovative solutions that help F&A teams achieve shorter close cycles and better controls, enabling them to drive better decision-making across the company. Outside of the accounting world, depreciation means the decline in value of an depreciation journal entry item after purchase. In accounting, depreciation is the process of allocating the cost of an item over its anticipated useful life. This helps to ensure that company revenues are matched with the costs of assets used by a company to generate that revenue.

Now that you understand the journalizing of depreciation, we’ll next turn to look at the relationship between accumulated depreciation and depreciation expense. Some firms calculate depreciation from the middle of the month of purchase. For example, they treat an asset purchased on any day of the month as if it were purchased on the 15th day of the month. An asset purchase on September 1 would result in 3½ months of depreciation for that first year of service.
BlackLine Journal Entry Automation & Management Software
The method currently used by the IRS is the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS). Like double declining, sum-of-the-years is best used with assets that lose more of their value early in their useful life. The purpose of depreciation is to allocate the cost of a fixed or tangible asset over its useful life.
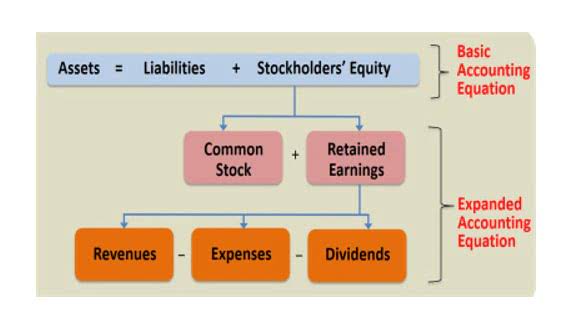
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra account, meaning it is attached to another account and is used to offset the main account balance that records the total depreciation expense for a fixed asset over its life.
- Accelerate adoption and drive productivity and performance.One of the critical success drivers for any software technology is effective user training and adoption.
- Kenzie pays shipping costs of $1,500 and setup costs of $2,500, assumes a useful life of five years or 960,000 pages.
- Calculate the accumulated depreciation and net book value of the equipment at the end of the third year.
- On the other hand, the accumulated depreciation is an item on the balance sheet.
One unique feature of the double-declining-balance method is that in the first year, the estimated salvage value is not subtracted from the total asset cost before calculating the first year’s depreciation expense. However, depreciation expense is not permitted to take the book value below https://www.bookstime.com/ the estimated salvage value, as demonstrated in the following text. For example, on Jan 1, the company ABC buys a piece of equipment that costs $5,000 to use in the business operation. The company estimates that the equipment has a useful life of 5 years with zero salvage value.

